SSD data recovery: Flash wear leveling technology analysis
SSD data recovery frontier: Flash wear leveling technology analysis
In recent years, solid-state storage technology has been greatly developed. As the cost of large-capacity flash chips continues to decrease, more and more computers are using solid-state drives. At present, the SSD is mainly used to install an operating system in a computer to improve the speed and speed of the computer. From the big trend, SSDs and mechanical hard drives will coexist for a long time, and will gradually eat into the market of mechanical hard drives. Therefore, as a leading brand in the data recovery industry, Darth Technology, a data recovery company that often has to deal with hard drives, must pay close attention to the development of SSD technology and track the cutting edge of technology.
SSDs, U disks, memory cards, etc. all use Flash memory chips, and Flash itself consists of several blocks - Block, each block is divided into several physical pages - Page. A block is the smallest unit of erase operation, while reads and writes are in pages. The figure below shows the storage structure of Flash.
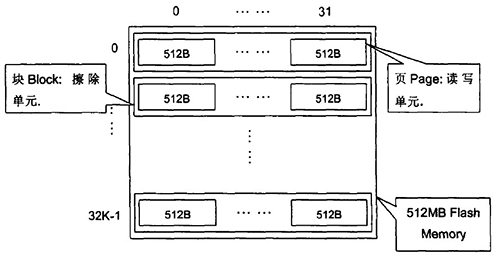
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of Flash storage structure
Flash takes an off-site update strategy, and the updated data is placed on other physical pages instead of overwriting the original data. The page containing the new version data is called a valid page, and the new version data is called valid data. A page containing old version data is called an invalid page, or a dirty page, and a dirty page can be rewritten after it becomes a free page after being erased. Because Flash is erased in units of blocks, it is necessary to erase all physical pages on the block where the dirty page is located. Before erasing, it is necessary to check whether there is a valid page on the block. If it exists, it must be transferred to other On the block. Because the number of erasures per Flash block is limited, generally between 100,000 and 1 million, as long as the number of erasures of a block reaches the upper limit, the performance of Flash data storage will decrease. Therefore, we must find a way to make the erase operation work on each flash block on average. This method is the wear-leveling algorithm.
When we apply Flash, we actually access the logical address of Flash. There is a mapping relationship between the logical address and the physical address, as shown in the following figure.
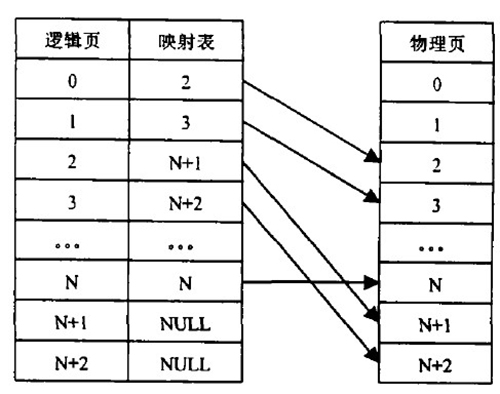
Figure 2 Flash storage mapping table
After the data is updated, it is only necessary to change the address of the physical page in the mapping table, and mark the physical page where the original version data is located as invalid. For data blocks that are frequently updated, we call them "hot" data blocks, and for data blocks that are not updated for a long time, they are called "cold" data blocks. If the data block is updated frequently, it will be erased frequently, and the data block that has not been processed for a long time will be erased without dirty pages, and the number of erasures will be significantly less than the block storing the frequently updated data. How to realize the exchange of "hot and cold" data storage location is a problem to be considered in the wear leveling process.
At present, the commonly used wear leveling algorithms are roughly divided into two categories, one is a random algorithm and the other is a deterministic algorithm. For the randomness algorithm, the principle is: after each write or erase operation, the wear leveling process is triggered according to a certain probability. According to the probability of uniform distribution, a block is randomly selected to perform an erase operation. Regardless of whether the block has "cold" data or "hot" data, each block gets an equal chance of being erased. Finally, the valid data on the selected block is copied to the empty block and the block is erased. Which free block to move the data to is also randomly selected, because there is no erasing of the recorded block, there is a case where the "cold" data is moved to a "cold" block again, and as a result, the block does not increase the number of erasures. This happens especially in systems with a lot of "cold" data.
For the deterministic algorithm, it is divided into two kinds of periodicity and globality. The principle of the periodic algorithm is: the life of the Flash is regarded as one wear and tear equalization period. During a processing cycle, the block that reaches the specified number of erasures will not be selected during this cycle, so that each block can reach the same number of erasures before starting the next erase cycle. By adjusting the number of erases of the Flash block, the entire Flash can achieve the desired wear leveling. The principle of the global algorithm is to control the wear level of the block in a global scope without dividing the processing cycle. When the difference between the erasure times of any two blocks exceeds a given threshold, or when the number of erasures of a block exceeds the average number of erasures of all blocks, the wear leveling process is started, and the block with less erasure is performed. The data on the data is exchanged with the data on the block with a large number of erasures. If the block stores "cold" data, that is, the data is rarely updated, the data on the block is not easily dirty and rarely gets erased. Conversely, if the block stores "hot" data, the data on that block is often updated, often with the opportunity to erase dirty data. According to this principle, "hot and cold" data is exchanged to achieve wear leveling.
Comparing the two types of wear leveling algorithms, it can be seen that the effect of the randomness algorithm is greatly affected by random factors. Before erasing, it is not known that each block is erased, and the random request for logical pages cannot be done. To complete equivalence, so although the randomness algorithm selects the processing page with equal probability, the number of erasures of each block does not reach the equal probability distribution, and a good wear leveling effect cannot be achieved. Since the deterministic algorithm records the number of erasures of the physical block, the adjustment decision can be made according to the information in the processing, and the blocks basically reach the similar erasure times, and the wear leveling effect is obviously better than the random algorithm. But this is achieved on the basis of a large amount of memory overhead.
According to the above discussion, it can be seen that the advantages of the two types of algorithms must be combined to achieve a better wear leveling process, in order to ensure the read and write speed of the Flash, and to ensure the service life of the Flash, which will determine the solid state. Whether storage can fully defeat the key battle of mechanical hard drives.
About Darth Technology
Darth Technology, a national high-tech enterprise, the only collaboration unit for the data recovery of the confidentiality of the Tianjin State Secrecy Bureau, the famous brand in the data recovery industry, leading the data recovery technology in China and even in Asia!
Darth Technology China Data Recovery and Forensics Experts! Hotline
More data recovery and forensics cutting-edge technology, please pay attention to WeChat public account: woocs
Micro signal: woocs

Long press to identify the QR code
Focus on data recovery and forensics technology, the Internet
Submission:
Peripheral Devices and Consumables
Based on the low labor cost and reasonable stainless steel cost, Helper help to offer clients internal transport devices with best price. These machines and device include standard material truck, smoking trolley, lifter, conveyer belts, spiral feeding machine, hydraulic lifter etc. The internal transport device is used in filling and forming workshop, tumbling and seasoning workshop, smoking and cooking room etc.

Helper has a professional team to design and produce sausage clips. They have rich experience and understand all the key points for produce good quality clips. From the raw material purchasing to mould designing, from the QC in production to post-treatment, they pay attention to all these details that lead to the good quality of Helper`s clip series. Our clips products include U shape clips, Great wall shape clips, and aluminum wire (for aluminum wire clipper).

U Shape Sausage Clip,Clips On Strip,Bag Packaging Clips,Screw Material Conveyor
Helper Machinery Group Co., Ltd. , https://www.ihelpergroup.com